说明:本文所参照的源码是jdk1.8
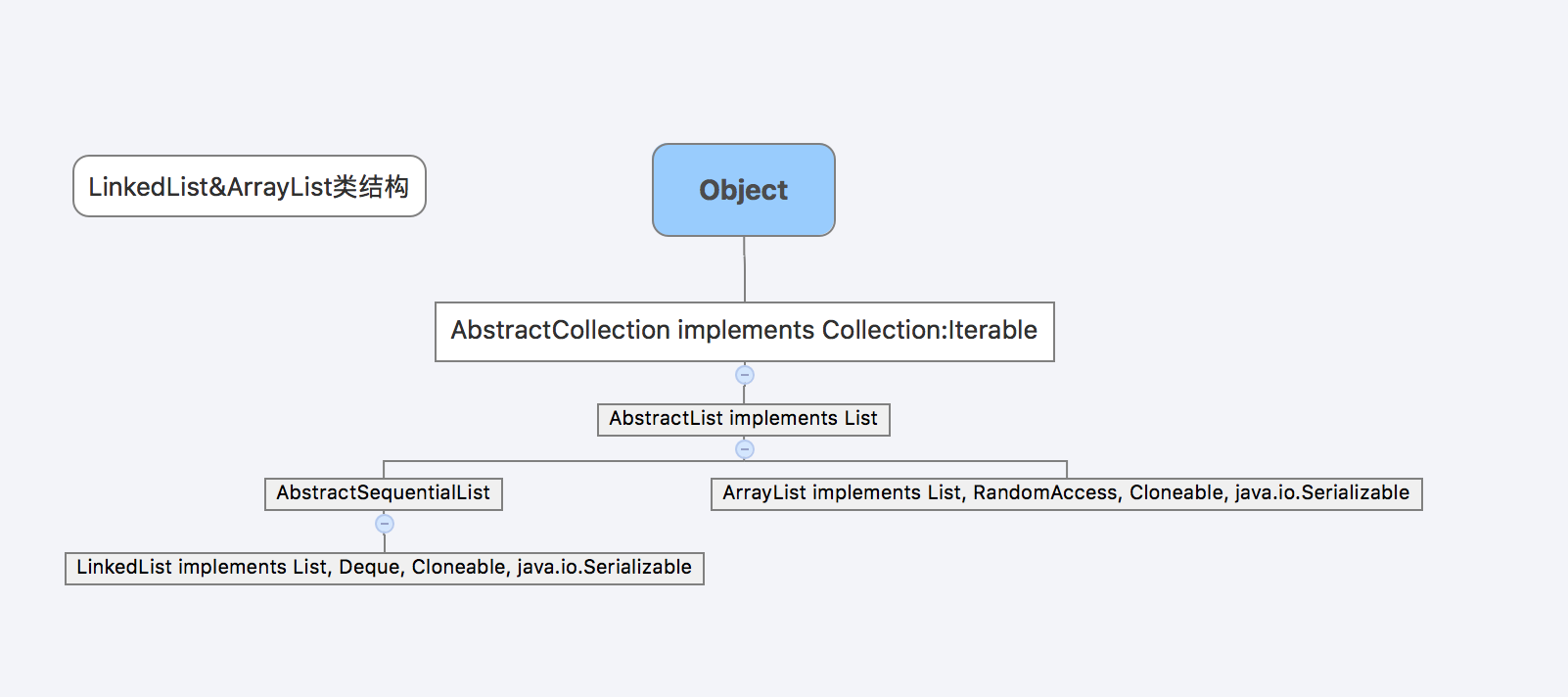
继承关系
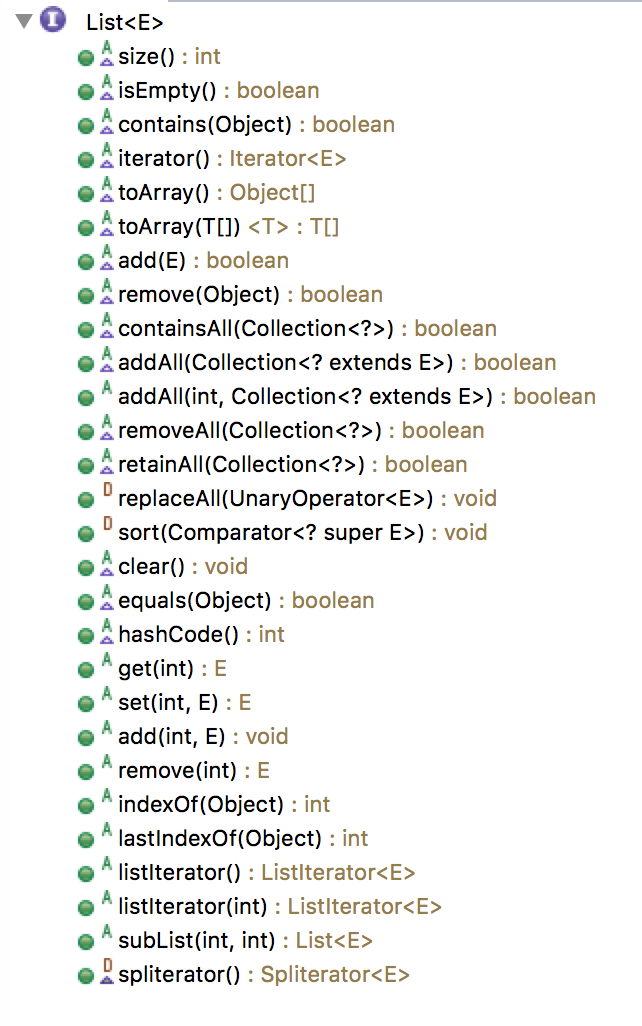
List接口提供的方法(28个)
相同点
- 都可被克隆和序列化,且都实现了List接口中定义的方法
- 实现了相同的hashcode算法
- 实现了相同的toString方法
不同点
- 数据结构不同
ArrayList是数组数据结构
LinkedList是链表结构
- 数据初始内存大小和插入性能不同
ArrayList内部数组扩展大小的算法(当前元素数组长度+它的二分之一,如,当前为30,扩展一次则变为45=30+30/2)
ArrayList初始创建时大小也为0(但可以通过构造方法指定大小),但是当往ArrayList中任意添加元素它的大小则会改变,当元素个数小于10则为10,当元素个数大于10,则按照扩展算法进行扩展;
LinkedList初始创建大小为0,因为数据结构是链表所以没有指定大小的构造函数。
因此,插入数据从性能上讲,LinkedList比ArrayList好,因为,LinkedList添加元素只要改变链表的前,后节点关系即可,而ArrayList要先检查数组大小处理扩展逻辑和拷贝数据到新的数组。
- 访问元素的性能对比
ArrayList通过数组下标访问,速度很快;LinkedList则有可能需要遍历整个链表一半的元素才能找到想要的元素
- LinkedList可实现队列
LinkedList实现了Deque接口,提供诸如push,pop,offer等方法,因此,它能很好地实现队列操作;而ArrayList并没有提供这些方法,由于它的数据结构决定了它也不适合作队列。
引申分析Vector
Vector从实现结构上跟ArrayList是一样的,区别在于Vector是线程安全的,ArrayList则不是。
Vector可以获取容积大小,而ArrayList获取不了
引申分析Set
- HashSet为数据结构为HashMap,因此,数据元素不会重复,也没有顺序
- LinkedHashSet的数据结构则为LinkedHashMap, 因此,数据元素依然不会重复,但双向链表就可以实现有序了